Techniques For Land Analysis have revolutionized the field of surveying, providing new tools and methods for understanding and analyzing land use and land cover. These techniques utilize remote sensing technologies and data to detect changes in land use over time, providing valuable insights for urban planning, agricultural land use, and sustainable land management. This article explores the groundbreaking techniques and methods used in land analysis, shedding light on the future of surveying.
Key Takeaways:
- Land analysis techniques have transformed the field of surveying, enabling a deeper understanding of land use and land cover.
- Remote sensing technologies play a pivotal role in gathering data and information about changes in land use over large areas.
- Geographic Information Systems (GIS) are essential tools for collecting, storing, and analyzing spatial data related to land use and land cover.
- Machine learning methods provide powerful algorithms and statistical models for analyzing large datasets and identifying patterns in land use.
- Spatial analysis techniques allow surveyors to evaluate the suitability of land for different purposes.
The Role of Remote Sensing in Land Analysis
Remote sensing plays a pivotal role in land analysis, providing surveyors with valuable data and insights into land use and land cover changes over large areas. This technology utilizes satellite imagery and aerial photography to capture detailed images of the Earth’s surface. These images are then analyzed to detect changes in land use and land cover, allowing for a comprehensive understanding of how the land is being utilized.
One of the key advantages of remote sensing is its ability to classify different land cover types. Through the analysis of satellite images, surveyors can identify and categorize various types of land cover, such as forests, urban areas, agricultural fields, and water bodies. This classification process is essential for mapping and monitoring changes in land cover over time.
Another important application of remote sensing in land analysis is the assessment of land surface temperature. By analyzing thermal images captured by satellites, surveyors can evaluate the temperature distribution across different land areas. This information can be used to identify areas with higher temperature levels, which may indicate heat islands or areas experiencing significant land use changes.
In the words of Dr. Jane Carter, a leading expert in remote sensing: “Remote sensing provides a unique perspective on our changing planet, allowing us to observe and monitor land use changes on a large scale. This technology is essential for understanding the complexities of our dynamic environment and making informed decisions for sustainable land management.”
The integration of remote sensing with other land analysis techniques, such as geographic information systems (GIS), further enhances its capabilities. By combining remote sensing data with GIS data, surveyors can create comprehensive maps and visualize land use changes in a spatial context. This integration enables a more holistic approach to land analysis, considering both the spatial and temporal aspects of land dynamics.
Overall, remote sensing plays a vital role in land analysis by providing surveyors with essential data on land use changes, land cover classification, and land surface temperature. This technology offers a powerful tool for understanding the complexities of our changing environment and facilitates informed decision-making for sustainable land management.
Using GIS for Land Analysis
The analysis of land requires advanced tools and technologies to gather and process data effectively. Among these tools, Geographic Information Systems (GIS) have emerged as a cornerstone in land analysis, providing surveyors with comprehensive spatial data collection and analysis capabilities.
GIS allows surveyors to collect and store spatial data related to land use and land cover. With this data, various analysis techniques can be employed to gain valuable insights. One prominent application is land use suitability analysis, which helps planners and decision-makers identify the most appropriate land use for different areas.
Change detection techniques are another critical aspect of land analysis, and GIS plays a vital role in detecting and monitoring changes in land use over time. By comparing different datasets acquired at different intervals, GIS enables surveyors to identify and analyze land cover changes accurately.
Moreover, GIS facilitates land use classification by categorizing different types of land use based on specific criteria and attributes. This classification allows for better understanding and management of land resources.
Integrating GIS with other technologies, such as remote sensing, can further enhance the capabilities of land analysis. By combining GIS data with remote sensing images, surveyors can perform detailed land cover change detection and analysis, providing holistic insights into land dynamics.
“The integration of GIS and remote sensing has significantly improved the accuracy and efficiency of land analysis. By combining spatial data with high-resolution imagery, surveyors can gain a comprehensive understanding of land use and land cover changes.”
Furthermore, GIS offers spatial analytical tools that enable surveyors to examine the relationships and patterns of land use and land cover at a detailed level. These tools consider factors such as elevation, slope, and proximity to evaluate the suitability of land for various purposes, ensuring sustainable land management.
Overall, GIS is an indispensable tool in land analysis, providing surveyors with the means to collect, store, analyze, and visualize spatial data. It empowers informed decision-making, facilitates land use planning, and enables effective land management strategies.
| Advantages of GIS in Land Analysis | Applications |
|---|---|
| Comprehensive collection and storage of spatial data | Land use suitability analysis |
| Accurate detection of land use changes over time | Change detection techniques |
| Categorization of land use based on specific criteria | Land use classification |
| Integration with remote sensing for detailed analysis | Combining GIS with remote sensing |
| Examination of spatial relationships and patterns | Spatial analysis techniques |
Machine Learning Methods in Land Analysis
Machine learning methods have revolutionized the field of land analysis by harnessing the power of algorithms and statistical models to analyze large datasets. These techniques enable surveyors to identify patterns and trends in land use and land cover, providing valuable insights for decision-making processes.
One of the key applications of machine learning in land analysis is land use suitability assessment. By training models on historical land data and incorporating various environmental factors, machine learning algorithms can evaluate the suitability of land for different purposes. This approach assists urban planners, environmental agencies, and land developers in making informed choices regarding land use and development.
Moreover, machine learning methods play a crucial role in change detection. By comparing satellite imagery and other spatial data collected at different time periods, these algorithms can detect and quantify changes in land use over time. This information is vital for monitoring land management efforts, understanding the impact of human activities on the environment, and predicting future land use patterns.
“Machine learning methods enable surveyors to harness the power of data to gain actionable insights, contributing to sustainable land management practices.”
These machine learning methods leverage a variety of techniques such as supervised learning, unsupervised learning, and deep learning. Supervised learning algorithms, for example, can be trained to classify land cover types based on labeled samples, enabling robust land cover classification. Unsupervised learning methods, on the other hand, can identify clusters and patterns within unlabeled datasets, facilitating the discovery of hidden relationships in land use data. Deep learning algorithms, with their ability to process and analyze complex spatial data, have shown promise in advancing land analysis capabilities.
The integration of machine learning with remote sensing and GIS technologies further enhances the accuracy and efficiency of land analysis. By combining machine learning algorithms with remote sensing images and GIS data, surveyors can achieve more comprehensive and detailed land analysis results. This integration allows for a multidimensional approach to land analysis, considering factors such as topography, climate, and vegetation indices, ultimately improving the understanding of land dynamics and aiding sustainable land management efforts.
Machine Learning Methods in Land Analysis: Key Benefits
- Efficient assessment of land suitability for different purposes.
- Accurate detection and monitoring of land use change over time.
- Improved land management and planning processes.
- Enhanced decision-making for sustainable development.
Machine learning methods have revolutionized land analysis, empowering surveyors with advanced tools for understanding and managing land use and land cover. These techniques, when integrated with remote sensing and GIS technologies, provide a comprehensive and data-driven approach to land analysis, enabling informed decision-making for sustainable land management.
Spatial Analysis Techniques for Land Analysis
Spatial analysis techniques play a crucial role in land analysis, providing surveyors with valuable insights into the spatial relationships and patterns of land use and land cover. By analyzing various spatial data, such as elevation, slope, and proximity, these techniques enable the evaluation of land suitability for different purposes. With spatial analysis, surveyors can assess the viability of land for urban development, agriculture, conservation, and other land use categories. This information is essential for land evaluation and planning processes, ensuring the sustainable utilization of land resources.
Identifying Spatial Relationships
One key aspect of spatial analysis is identifying the spatial relationships between different land features. By examining the proximity of land parcels to urban centers, transportation networks, water bodies, and other significant factors, surveyors can assess their suitability for specific purposes. For example, analyzing the proximity of land parcels to transportation networks can determine their potential for residential or commercial development.
Evaluating Land Suitability
Land suitability analysis is another crucial part of spatial analysis techniques. Surveyors use various criteria, such as soil quality, topography, and climatic conditions, to evaluate the suitability of land for different purposes. This analysis helps determine the most appropriate land use for various areas, ensuring optimal utilization and minimizing potential environmental impacts.
For example, by considering soil fertility, drainage, and other agricultural factors, surveyors can identify the most suitable areas for agriculture. Similarly, by assessing the ecological value and biodiversity of different land parcels, surveyors can determine suitable areas for conservation and protected reserves.
Mapping and Visualizing Spatial Data
Spatial analysis techniques also involve the mapping and visualization of spatial data. Geographic Information Systems (GIS) allow surveyors to collect, store, and analyze data related to land use and land cover. By creating maps and visual representations of this data, surveyors can gain a comprehensive understanding of the spatial patterns and distributions of different land features.
These maps and visualizations assist in decision-making processes, as they provide a clear and concise representation of the suitability of land for specific purposes. Surveyors can identify areas with high potential for development, areas prone to natural hazards, or areas suitable for conservation efforts, among other purposes.
To illustrate the importance of spatial analysis techniques in land analysis, consider the example map below:
This map showcases how spatial analysis can identify suitable areas for different land uses, such as residential, commercial, and agricultural purposes. By utilizing spatial analysis techniques, surveyors can make informed decisions about land use planning and management, promoting sustainable development and ensuring the efficient use of land resources.
Integration of Remote Sensing and GIS in Land Analysis
The integration of remote sensing and GIS has revolutionized land analysis, providing surveyors with powerful tools to understand and analyze the dynamics of land use and land cover. By combining remote sensing images with GIS data, surveyors can gain valuable insights into land cover change detection, enabling them to identify areas where land use and land cover have transformed over time.
This integrated approach also facilitates comprehensive land-use planning and analysis, considering various factors such as environmental impact, socio-economic considerations, and land suitability. By leveraging remote sensing images and GIS data, surveyors can evaluate land-use options, assess the impact of proposed developments, and make informed decisions regarding land management.
The combination of remote sensing and GIS supports an interdisciplinary approach to land analysis, allowing surveyors to consider multiple perspectives and factors when analyzing land dynamics. This holistic understanding enhances the accuracy and effectiveness of land analysis, enabling sustainable land-use practices.
Furthermore, remote sensing and GIS integration enables the visualization and spatial representation of land data, aiding in the communication of analysis results. By creating maps, charts, and visualizations, surveyors can effectively communicate land-use patterns and changes to stakeholders, facilitating better decision-making and engagement.
The image below exemplifies the integration of remote sensing and GIS in land analysis:
Multitemporal Analysis Methods in Land Analysis
Multitemporal analysis methods are crucial for gaining a comprehensive understanding of land use and land cover changes over time. By comparing and analyzing different datasets acquired at various points in time, surveyors can utilize powerful techniques such as change vector analysis and multiple endmember spectral mixture analysis to unearth valuable insights. These multitemporal analysis methods allow for the exploration of trends, patterns, and drivers of change in land use and land cover.
Change Vector Analysis
Change vector analysis, a popular multitemporal analysis technique, quantifies the magnitude and direction of changes in land use and land cover. By comparing spectral information between different time periods, change vector analysis identifies and measures the extent of changes that have occurred. This technique aids in the detection of areas experiencing rapid land use transitions, providing crucial information for land management and decision-making processes.
Multiple Endmember Spectral Mixture Analysis
Multiple endmember spectral mixture analysis enables surveyors to identify different land cover components within each pixel of a remotely sensed image. By analyzing the spectral responses of materials present in the image, this technique can determine the fractional abundance of each land cover component. Multiple endmember spectral mixture analysis offers detailed insights into the composition and distribution of land cover types, contributing to land use planning, ecological studies, and environmental monitoring.
By leveraging multitemporal analysis methods such as change vector analysis and multiple endmember spectral mixture analysis, surveyors gain a comprehensive understanding of the dynamics of land use and land cover. The insights garnered from these techniques aid in effective monitoring and management of land resources, supporting sustainable land practices that ensure harmony between human activities and the environment.

Historical Approaches to Land Analysis
Historical land analysis has greatly influenced modern surveying techniques, laying the foundation for the field’s advancements. Surveying pioneers like William Clark and Colonel John James Abert made significant contributions to land analysis through their innovative surveying techniques and methodologies.
These pioneers played a crucial role in mapping and analyzing land in different regions, employing various surveying techniques to gather essential data. Their historical approaches encompassed land survey techniques, spatial analysis methods, and cartographic mapping.
By studying the historical development of land analysis, surveyors today can gain a deeper understanding of the evolution of surveying techniques and practices. These insights not only provide valuable historical context but also offer valuable lessons that can be applied to modern land analysis methodologies and challenges.
“The history of land analysis is a testament to the ingenuity and determination of surveyors who paved the way for modern surveying techniques. It’s crucial that we acknowledge and learn from their contributions to further advance our understanding of land dynamics.” – Surveying expert.
Exploring historical land analysis not only sheds light on the evolution of surveying techniques but also helps surveyors appreciate the foundational principles that underpin modern land analysis. Understanding the techniques and methodologies employed by surveying pioneers enhances the knowledge and skills necessary for effective land surveying today.
Key Surveying Pioneers
Let’s take a closer look at two influential surveying pioneers:
- William Clark: As a member of the Lewis and Clark Expedition, Clark played a significant role in mapping and analyzing land in the early 19th century. His meticulous surveying techniques and mapping expertise provided important insights into the geography and topography of previously unexplored territories.
- Colonel John James Abert: Abert’s contributions to land analysis focused on the coastal regions of the United States. His surveying techniques and cartographic mapping skills were crucial in gathering land-related data and documenting coastal features. Abert’s work laid the groundwork for future coastal land analysis and management.
These surveying pioneers, among others, were trailblazers in their field and made lasting contributions to the development of land analysis techniques. Their work and innovations paved the way for the sophisticated surveying methods used today.
Understanding the Evolution of Land Survey Techniques
The historical development of land analysis provides valuable insights into the evolution of surveying techniques. From early compass and chain surveys to the modern use of advanced technologies like GPS and LiDAR, the field has progressed significantly.
By examining historical surveying methods, surveyors gain a comprehensive understanding of the challenges faced by early land analysts and the creative solutions they devised. This knowledge helps inform and enhance contemporary surveying approaches, ensuring accuracy and reliability in understanding land dynamics.

The Future of Land Analysis
While modern surveying techniques continue to evolve and incorporate new technologies, it is essential to acknowledge the contributions of historical land analysis. By studying the techniques and approaches of surveying pioneers, surveyors can build upon their legacy and contribute to the ongoing progress of land analysis.
The historical foundations of land analysis remind us of the enduring importance of accurate data collection, meticulous mapping, and spatial analysis. By maintaining an appreciation for historical approaches while embracing technological advancements, surveyors can forge a path toward a future of innovative and sustainable land analysis.
Advancements in Land Analysis Technologies
Advancements in technology have propelled land analysis to new heights. Environmental analysis tools, such as Geographic Information Systems (GIS) and remote sensing, have become more sophisticated and user-friendly, enabling surveyors to efficiently collect, manage, and analyze land-related data.
GIS mapping for land analysis provides comprehensive geospatial information, allowing surveyors to visualize and understand land-use patterns and changes over time. With GIS, surveyors can create detailed maps, perform spatial analysis, and conduct land suitability assessments. This technology revolutionizes land analysis by providing a holistic view of the landscape, facilitating informed decision-making for land management and conservation.
Remote sensing technologies offer a wealth of detailed imagery and data about land use and land cover. Satellites and aerial sensors capture high-resolution images, which can be used to monitor and assess changes in vegetation, land surface temperature, and other environmental variables. Remote sensing enables surveyors to detect patterns, identify trends, and evaluate the impact of human activities on the land. It enhances the accuracy and efficiency of land analysis, advancing our understanding of the Earth’s dynamic landscapes.
“The integration of GIS mapping and remote sensing technologies has revolutionized land analysis, providing surveyors with powerful tools to study and manage our changing environment.”
NASA’s Landsat Program
An exemplary application of remote sensing in land analysis is NASA’s Landsat program. This long-running initiative, which began in 1972, provides a continuous record of Earth’s changing landscapes through a series of satellites equipped with multispectral sensors. The Landsat data has been instrumental in monitoring land use, vegetation health, water resources, and urban growth. Surveyors and scientists around the world rely on Landsat images to study and protect the planet’s valuable ecosystems.
Also Read:- Navigating Concerns: Understanding Worries Surrounding Technology Development
Through these advancements in land analysis technologies, surveyors can acquire accurate, up-to-date information about the Earth’s surface and its transformations. This knowledge supports better land management practices, sustainable development, and informed decision-making for a wide range of sectors, including agriculture, urban planning, natural resource conservation, and disaster management.
The image below showcases the power of remote sensing in land analysis, capturing the dynamic interplay between urban development, agriculture, and natural landscapes.
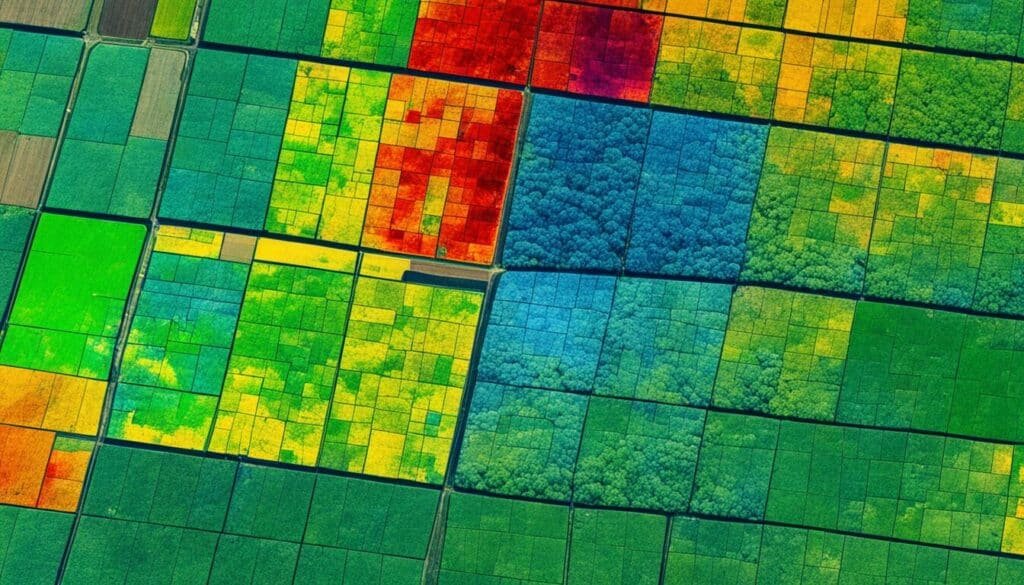

Conclusion
Land analysis techniques have revolutionized the field of surveying, providing surveyors with innovative tools and methods for understanding and analyzing land use and land cover. Remote sensing, GIS, machine learning, spatial analysis, and other technologies have played a crucial role in advancing land analysis capabilities.
By integrating these techniques and approaches, surveyors can gather comprehensive and accurate data about land dynamics, enabling informed decision-making and sustainable land management practices. These trailblazing techniques have not only enhanced the accuracy and efficiency of land analysis but also paved the way for more holistic and interdisciplinary approaches in the field of surveying.
The future of surveying heavily relies on these trailblazing techniques, which continue to evolve and shape the field. As technology advances and new methodologies emerge, surveyors will have even more powerful tools at their disposal to analyze land and make informed decisions that promote sustainable land use and management.
FAQs
A: Land cover classification is the process of categorizing and mapping different types of land cover, such as forests, grasslands, urban areas, and water bodies, using remote sensing data and GIS techniques.
Q: How is land use analysis conducted?
A: Land use analysis is conducted by examining the current land use patterns, identifying changes over time, and assessing the impact of human activities on the landscape using remote sensing images and geospatial tools,analysis process.
Q: What are the methods for land-use change detection?
A: Methods for land-use change detection include change detection techniques such as change-vector analysis, classification of land cover using remote sensing images, and analysis using GIS tools to track changes in land use types over time,land use change detection.
Q: What is the significance of land-use analysis in land management decisions?
A: Land-use analysis plays a crucial role in informing land management decisions by providing valuable insights into patterns of land use, identifying areas suitable for specific activities, and assessing the impact of land use changes on the environment,land-use type .
Q: How do GIS and remote sensing techniques contribute to land analysis?
A: GIS and remote sensing techniques are essential tools in land analysis as they enable the integration of spatial data, mapping of land cover and land use, and monitoring changes in the landscape over time with high accuracy and efficiency.
Q: What are the different categories of land use?
A: Different categories of land use include agricultural land, urban land, forested areas, water bodies, industrial zones, residential areas, and recreational spaces, each serving specific purposes and having distinct characteristics.
Q: How can land cover and land use change analysis benefit environmental conservation efforts?
A: Land cover and land use change analysis can benefit environmental conservation efforts by identifying areas undergoing significant changes, assessing threats to biodiversity, and guiding conservation strategies to protect valuable ecosystems and natural resources.
Q: What is land cover classification and its significance in surveying?
A: Land cover classification is the process of categorizing different types of surface cover present on the Earth’s surface, such as forests, urban areas, water bodies, and agricultural land. It is essential in surveying as it helps in understanding the distribution and composition of different land features for various analyses and decision-making processes.
Q: How do surveyors analyze land-use change?
A: Surveyors analyze land-use change by comparing historical data with current data to identify any alterations in the way the land is being utilized. This analysis helps in tracking changes in land patterns over time and understanding the impact of human activities on the environment.
Q: What are the common methods used for land cover classification using GIS and remote sensing techniques?
A: Common methods for land cover classification using GIS and remote sensing techniques include supervised classification, unsupervised classification, object-based image analysis, and change detection methods. These techniques leverage satellite images and geographic information systems to accurately classify and map different land cover types.
Q: How can surveyors detect land use changes using remote sensing images?
A: Surveyors can detect land use changes using remote sensing images by comparing multi-temporal satellite images taken at different time intervals. By analyzing these images, changes in land cover types, land use patterns, and urban expansion can be identified and monitored over time.
Q: What is the impact of land use decisions on the environment?
A: Land use decisions have a significant impact on the environment as they can lead to changes in ecosystems, loss of biodiversity, soil degradation, water pollution, and habitat destruction. It is crucial for surveyors to assess the implications of land use decisions to ensure sustainable development and conservation of natural resources.
Q: How is land reclamation performed, and what are its objectives?
A: Land reclamation is the process of converting degraded or unproductive land into usable land through various engineering and environmental techniques. The objectives of land reclamation include increasing the land’s productivity, restoring natural habitats, mitigating environmental pollution, and supporting sustainable development initiatives.
Q: What are the different categories of land use that surveyors analyze?
A: Surveyors analyze various categories of land use, including agricultural land, urban land, forest land, wetlands, water bodies, industrial land, residential areas, recreational areas, and transportation infrastructure. Understanding the distribution and dynamics of these land use categories is crucial for effective land management and planning.
Source Links
- https://www.ornl.gov/staff-profile/sumner-s-brown-gibbs
- https://www.cambridge.org/core/journals/british-journal-for-the-history-of-science/article/pettys-instruments-the-down-survey-territorial-natural-history-and-the-birth-of-statistics/0C35B4A6C753DE4DF81B523B4AD6B62B
- https://www.agc.army.mil/Who-we-are/History/